Austrialia
Department of Health and Ageing (DHA)
The Department of Health and Ageing has a diverse set of responsibilities, but throughout there is a common purpose, which is reflected in our Vision statement: Better health and active ageing for all Australians. We aim to achieve our Vision through strengthening evidence-based policy advising, improving program management, research, regulation and partnerships with other government agencies, consumers and stakeholders.
Office of the Gene Technology Regulator (OGTR)
The Office of the Gene Technology Regulator has been established within the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing to provide administrative support to the Gene Technology Regulator in the performance of her functions under the Gene Technology Act 2000.
The Gene Technology Act 2000, which came into force on 21 June 2001, introduces a national scheme for the regulation of genetically modified organisms in Australia, in order to protect the health and safety of Australians and the Australian environment by identifying risks posed by or as a result of gene technology, and by managing those risks through regulating certain dealings with genetically modified organisms.
China
Chinese Ministry of Public Health (CMPH)
An executive agency of the state which plays the role of providing information, raising health awareness and education, ensuring the accessibility of health services, and monitoring the quality of health services provided to citizens and visitors in the mainland of the People's Republic of China.
The MOH is also involved in the control of illness and disease, coordinating the utilisation of resources and expertise where necessary. It also cooperates and keeps in touch with other health ministries and departments, including those of the special administrative regions, and the World Health Organization (WHO).
State Food and Drug Administration of China (SFDA)
According to the restructuring plan of the State Council approved by the First Plenary Session of the 10th National People's Congress and "the State Council Notice on Government Structuring" (No.8.2003.), the State Food and Drug Administration is founded on the basis of the State Drug Administration. The State Food and Drug Administration is directly under the State Council, which is in charge of comprehensive supervision on the safety management of food, health food and cosmetics and is the competent authority of drug regulation.
European Union
European Medicines Agency (EMEA)
The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) is a decentralised body of the European Union with headquarters in London. Its main responsibility is the protection and promotion of public and animal health, through the evaluation and supervision of medicines for human and veterinary use.
Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
Enhance and safeguard the health of the public by ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe. No product is risk-free. Underpinning all our work lie robust and fact-based judgements to ensure that the benefits to patients and the public justify the risks.
Scientific Advisory Committee on Genetically Modified Organisms (ACGMO)
The Scientific Advisory Committee on Genetically Modified Organisms (Contained Use) - SACGM (CU) - provides technical and scientific advice to the UK Competent Authorities (UK CAs) on all aspects of the human and environmental risks of the contained use of genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Gene Therapy Advisory Committee (GTAC)
GTAC is the UK national research ethics committee (REC) for gene therapy clinical research according to the Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations 2004 (http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si2004/20041031.htm, see article 14(5)). It is the only UK ethics committee empowered to approve clinical trials of gene therapy products according to the definition given in Part IV of Directive 2003/63/EC (amending Directive 2001/83/EC).
United States
The Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS)
THE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES (HHS) is the United States government's principal agency for protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services, especially for those who are least able to help themselves.
The Office of Human Research Protections (OHRP)
The Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) protects the rights, welfare, and well-being of subjects involved in research conducted or supported by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and helps ensure that such research is carried out in accordance with the regulations described at 45 CFR part 46.
OHRP Links to Reference Documents
Human subject research conducted or supported by each federal department/agency listed below is governed by the regulations of that department/agency. The head of that department/agency retains final judgment as to whether a particular activity it conducts or supports is covered by the Common Rule. If an institution seeks guidance on implementation of the Common Rule and other applicable federal regulations, the institution should contact the department/agency conducting or supporting the research.
The federal department/agency that conducts or supports research retains final authority for determining whether an institution has complied with its regulations for the protection of human subjects. If HHS receives an allegation or indication of noncompliance related to human subject research that is conducted or supported solely by a Common Rule department/agency other than HHS, HHS will refer the matter to that department/agency for review and action as appropriate.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
The FDA is responsible for protecting the public health by assuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, medical devices, our nation’s food supply, cosmetics, and products that emit radiation. The FDA is also responsible for advancing the public health by helping to speed innovations that make medicines and foods more effective, safer, and more affordable; and helping the public get the accurate, science-based information they need to use medicines and foods to improve their health.
FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
CBER is responsible for ensuring the safety and efficacy of blood and blood products, vaccines, allergenics, and biological therapeutics. CBER's regulation of biological products has expanded in recent years to include a wide variety of new products such as biotechnology products, somatic cell therapy and gene therapy, and human cells, tissue and cellular and tissue-based products.
CBER Resources for Cellular and Gene Therapy
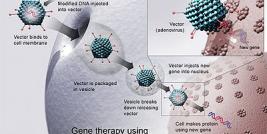
The Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) regulates human gene therapy products - products that introduce genetic material into the body to replace faulty or missing genetic material, thus treating or curing a disease or abnormal medical condition. CBER uses both the Public Health Service Act and the Federal Food Drug and Cosmetic Act as enabling statutes for oversight.
FDA has not yet approved any human gene therapy product for sale. However, the amount of gene-related research and development occurring in the United States continues to grow at a fast rate and FDA is actively involved in overseeing this activity. FDA has received many requests from medical researchers and manufacturers to study gene therapy and to develop gene therapy products. Such research could lead to gene-based treatments for cancer, cystic fibrosis, heart disease, hemophilia, wounds, infectious diseases such as AIDS, and graft-versus-host disease.
FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)
The Center for Drug Evaluation and Research's (CDER) job is to ensure that drugs are safe and effective. (See "Benefit vs. Risk: How FDA Approves New Drugs"). CDER does not test drugs, although the Center's Office of Testing and Research does conduct limited research in the areas of drug quality, safety, and effectiveness.
FDA Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH)
Like other components of FDA, the Center for Devices and Radiological Health has established advisory committees to provide independent, professional expertise and technical assistance on the development, safety and effectiveness, and regulation of medical devices and electronic products that produce radiation. Each committee consists of experts with recognized expertise and judgment in a specific field. Members have the training and experience necessary to evaluate information objectively and to interpret its significance. These persons are not regular employees of FDA, but are paid as "special government employees" for the days they participate as members of a panel. This is time they take from their daily occupations to provide their professional skills to FDA. The committees are advisory -- they provide their expertise and recommendations -- but final decisions are made by FDA.
The Center has four advisory committees, including a Medical Devices Advisory Committee which consists of 18 panels that cover the medical specialty areas. These advisory committee meetings are open to the public, and time is provided for public comment on the topic under consideration. Persons who wish to present their views must contact the executive secretary (listed here as the contact) and request time in advance. For additional information, call the FDA Advisory Committee Information Hotline at 1-800-741-8138 (in the Washington, D.C. area, call 301-443-0572).
The National Institutes of Health (NIH)
NIH is the steward of medical and behavioral research for the Nation. Its mission is science in pursuit of fundamental knowledge about the nature and behavior of living systems and the application of that knowledge to extend healthy life and reduce the burdens of illness and disability.
NIH Office of Biotechnology Activities (OBA)
- Monitors scientific progress in human genetics research in order to anticipate future developments, including ethical, legal, and social concerns, in basic and clinical research involving Recombinant DNA, Genetic Technologies, and Xenotransplantation;
- Manages the operation of, and provides analytical support to, the NIH Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee, the DHHS Secretary's Advisory Committee on Genetics, Health, and Society, and the DHHS Secretary's Advisory Committee on Xenotransplantation;
- Coordinates and provides liaison with Federal and non-Federal national and international organizations concerned with Recombinant DNA, Human Gene Transfer, Genetic Technologies, and Xenotransplantation;
- Provides advice to the NIH Director, other Federal agencies, and State regulatory organizations concerning Recombinant DNA research, Human Gene Transfer, Genetic Technologies, and Xenotransplantation;
- Responds to requests for information on highly technical matters and matters of public policy related to Recombinant DNA, Human Gene Transfer, Genetic Technologies, and Xenotransplantation;
- Develops and implements NIH policies and procedures for the safe conduct of Recombinant DNA Activities, and Human Gene Transfer;
- Reviews and evaluates the composition of Institutional Biosafety Committees; and
- Develops registries of activities related to Recombinant DNA Research and Human Gene Transfer.
NIH Office of Human Subjects Research (OHSR)
The OHSR is responsible for NIH-wide policy development, educational activities, oversight and coordination of NIH’s HRPP. The OHSR has been established to help NIH investigators understand and comply with ethical principles and regulatory requirements involved in human subjects research and to assist various NIH components in administering and regulating human subjects research activities so as to promote both the rights and welfare of human subjects and the NIH's research mandate.